Effective payroll management ensures legal compliance, accurate salary disbursement, and employee satisfaction. This guide covers the step-by-step payroll preparation process for companies operating in Delhi, considering applicable laws and state-specific requirements.

✅ Step 1: Understand Legal Framework in Delhi
In Delhi, payroll preparation must align with the following laws:
- Code on Wages, 2019 – Governs minimum wages, timely payment, and authorized deductions.
- Payment of Wages Act, 1936 – Mandates providing salary slips and defines payment methods.
- Shops & Establishments Act (Delhi) – Covers working hours, leaves, and employment conditions.
- Employee Provident Fund (EPF) Act, 1952 – Provides retirement benefits through PF contributions.
- Employee State Insurance (ESI) Act, 1948 – Offers medical and insurance benefits.
- Income Tax Act, 1961 – Requires deduction of TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) from employee salaries.
- Professional Tax (Delhi) – Not applicable (Delhi does not levy professional tax).
✅ Step 2: Employee Information Collection
Gather and maintain accurate employee data to ensure payroll accuracy.
Documents Required:
- PAN Card – For tax purposes.
- Aadhaar Card – Identity verification.
- Bank Account Details – For salary transfer.
- Joining Letter & Employment Contract – Defines salary structure and benefits.
- Attendance & Leave Records – Essential for salary calculations.
- Investment Declarations – For tax exemptions under Section 80C and other provisions.
✅ Step 3: Salary Structure Design
Design a CTC (Cost-to-Company)-based salary structure that aligns with legal mandates.
Sample Salary Structure:
| Component | Calculation Basis | Taxable (Yes/No) |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Salary | 40%-50% of CTC | Yes |
| House Rent Allowance | 40% of Basic (50% in Metro Cities) | Partially |
| Special Allowance | Remaining balance after other components | Yes |
| Conveyance Allowance | ₹1,600/month (exempt up to this limit) | Partially (If > ₹1,600) |
| Medical Allowance | ₹15,000/year (if claimed) | Partially |
| Employer PF Contribution | 12% of Basic (Statutory requirement) | No |
| ESI Contribution | 3.25% of Gross (if applicable) | No |
| Bonus (if applicable) | Minimum 8.33% of Basic (for eligible staff) | Yes |
✅ Step 4: Payroll Calculation Process
- Gross Salary Calculation:
Formula:
Basic + HRA + Special Allowance + Other Allowances - Deductions Calculation:
a) Employee Provident Fund (EPF): 12% of Basic Salary (if monthly wages ≤ ₹15,000).
b) Employee State Insurance (ESI): 0.75% of Gross (for wages ≤ ₹21,000/month).
c) Tax Deducted at Source (TDS): As per Income Tax Slabs.

✅ Step 5: Payroll Compliance Checklist
- EPF Compliance:
- Register with EPFO – Mandatory for companies with 20+ employees.
- Monthly Filing – File EPF Returns (Form 5, Form 10, Form 12A) by the 15th.
- ESI Compliance:
- Register if the company has 10+ employees with wages below ₹21,000/month.
- ESI Contribution Payment – By the 15th of every month.
- TDS Compliance:
- Deduct TDS based on Section 192 of the Income Tax Act.
- File Form 24Q quarterly and issue Form 16 annually.
- Shops & Establishments Act:
- Ensure compliance with working hours (max 9 hours/day, 48 hours/week).
- Maintain leave records and provide salary slips.
✅ Step 6: Salary Payment Process
- Approval Workflow:
- HR calculates payroll and seeks management approval.
- Bank Transfer:
- Ensure salary disbursement via NEFT/RTGS/IMPS before the 7th of the month.
- Issue Salary Slips:
- Provide digital or printed payslips to all employees.
✅ Step 7: Record-Keeping & Audits
Maintain these records for 7 years as per legal mandates:
- Employee-wise payroll registers.
- EPF & ESI contribution records.
- Tax compliance (TDS certificates).
- Salary disbursement records.
✅ Step 8: Annual Payroll Activities
- Form 16 Distribution: Provide Form 16 by June 15th annually.
- Tax Proof Verification: Validate employee declarations (80C, HRA) before March 31st.
- Audit Preparation: Ensure compliance with all labour laws through internal audits.
✅ Step 9: Key Payroll Deadlines in Delhi
| Task | Due Date |
|---|---|
| Salary Payment | By the 7th of next month |
| EPF Contribution | By the 15th of each month |
| ESI Contribution | By the 15th of each month |
| TDS Payment (Form 24Q) | By the 7th of each month |
| Annual Form 16 Issue | By June 15th |
✅ Step 10: Tools for Payroll Management
- Payroll Software – Zoho Payroll, GreytHR, RazorpayX.
- EPFO & ESIC Portals – For compliance filings.
- Income Tax e-Filing Portal – For TDS submissions.
Let’s take an example, in which a person has worked for 24 days in a month and has taken 2 days absents or unpaid leaves as well as has worked 20 hours overtime during the month:
This detailed guide walks through the payroll calculation process in Delhi with an example, including regular salary, overtime, statutory deductions (EPF, ESI, TDS), and how to stay legally compliant.
✅ Step 1: Gather Employee Data for Payroll Calculation
For accurate payroll preparation, collect the following details:
- Basic Salary: ₹30,000/month
- HRA (House Rent Allowance): ₹12,000/month (40% of Basic in Delhi)
- Other Allowances (Conveyance, Special Allowance, etc.): ₹8,000/month
- Working Days in the Month: 26 Days (Industry standard)
- Employee Attendance: 24 Days Worked + 2 Days Leave (Unpaid)
- Overtime: 20 Hours Worked
- EPF: Employer & Employee – 12% of Basic (Mandatory for companies with 20+ employees)
- ESI: Employer – 3.25%, Employee – 0.75% (Mandatory for wages ≤ ₹21,000/month)
- TDS: Based on Income Tax Slabs
- Working Hours/Day: 8 Hours
✅ Step 2: Calculate Gross Salary
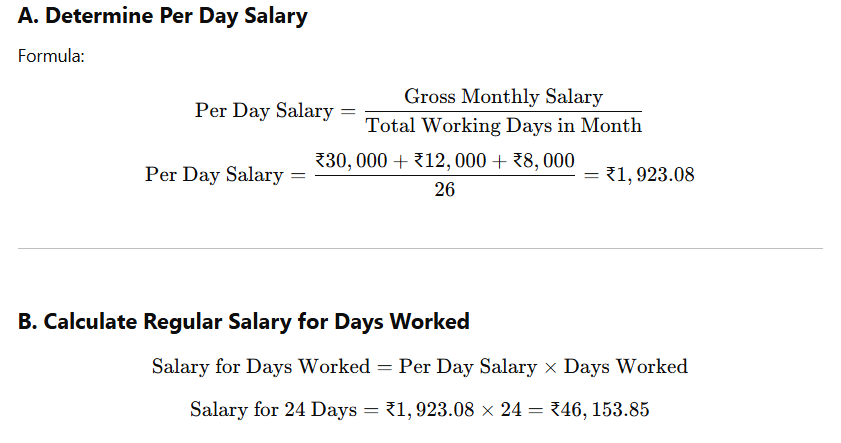

✅ Step 3: Calculate Statutory Deductions

B. ESI (Employee State Insurance)
Since the Gross Salary exceeds ₹21,000/month, ESI is not applicable.
C. TDS (Tax Deducted at Source)
Annual Salary Projection:
Annual Salary=₹55,769.23×12=₹6,69,230.76
For FY 2023-24, the applicable Income Tax Slab under the new regime:
| Annual Income (₹) | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to ₹3,00,000 | Nil |
| ₹3,00,001 – ₹6,00,000 | 5% |
| ₹6,00,001 – ₹9,00,000 | 10% |
| ₹9,00,001 – ₹12,00,000 | 15% |
- Taxable Income Calculation:
Taxable Income=₹6,69,230.76−₹50,000(Standard Deduction)=₹6,19,230.76
- TDS Calculation:
TDS=₹19,230.76×10%=₹1,923.08
✅ Step 4: Calculate Net Salary (In-Hand Salary)
Formula: Net Salary=Gross Salary−(EPF (Employee)+ESI (if applicable)+TDS)
Net Salary=₹55,769.23−(₹3,600+₹1,923.08)=₹50,246.15
✅ Step 5: Summary – Payroll Calculation Example
| Component | Amount (₹) |
|---|---|
| Basic Salary | ₹30,000 |
| HRA (40% of Basic) | ₹12,000 |
| Other Allowances | ₹8,000 |
| Overtime Pay (20 hrs) | ₹9,615.38 |
| Total Gross Salary | ₹55,769.23 |
| Deductions: | |
| – EPF (Employee – 12%) | ₹3,600 |
| – ESI | Not Applicable |
| – TDS | ₹1,923.08 |
| Net Salary (In-Hand) | ₹50,246.15 |
| Employer’s EPF Contribution | ₹3,600 |
✅ Step 6: Payroll Reporting & Compliance Deadlines
| Task | Due Date |
|---|---|
| Salary Payment | By the 7th of the next month |
| EPF Payment | By the 15th of the month |
| TDS Payment | By the 7th of the following month |
| Issue Salary Slips | Monthly (Mandatory) |
| Annual Form 16 Issue | By June 15th |
✅ Step 7: Payroll Best Practices in Delhi
- Accurate Time Tracking – Use attendance software to calculate work hours and overtime.
- Statutory Compliance – Stay updated with changes in EPF, ESI, and Tax rules.
- Audit Trails – Keep payroll records for at least 7 years for inspection.
