The Best Ways to Measure Productivity of Employees: A Comprehensive Guide
Employee productivity is a critical factor in organizational success. Understanding how to accurately measure productivity allows managers to make data-driven decisions, optimize processes, and improve overall performance. However, measuring productivity isn’t one-size-fits-all; it requires a comprehensive approach that accounts for job types, industries, and organizational goals. This article discusses the best ways to measure employee productivity, drawing from research and practical frameworks, while incorporating tables and charts for better understanding.
1. Quantitative Metrics of Productivity
Quantitative metrics provide tangible measures of output, making them easy to track and analyze. Here are some effective quantitative methods:
1.1. Output Per Hour (OPH)
Output per hour is one of the simplest ways to measure productivity. This metric evaluates how much work an employee accomplishes in a given hour.
Formula:
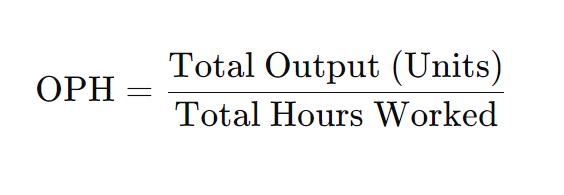
Example:
| Employee | Units Produced | Hours Worked | Output per Hour (OPH) |
| John | 200 | 25 | 8 |
| Alice | 220 | 30 | 7.33 |
| Bob | 150 | 20 | 7.5 |
This method works well for industries such as manufacturing, where output is clear and measurable.
1.2. Sales Metrics
In sales-based organizations, productivity can be directly tied to sales figures, such as:
- Sales Revenue Per Employee: The amount of revenue each employee generates.
- Number of New Clients: Measuring the new clients acquired per salesperson.
Example:
| Salesperson | Sales Revenue | Clients Acquired | Sales per Client ($) |
| Emily | $50,000 | 25 | 2,000 |
| David | $70,000 | 30 | 2,333 |
| Sarah | $60,000 | 20 | 3,000 |
1.3. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
KPIs are specific metrics used to gauge an employee’s performance in relation to their job role.
Common KPIs:
- Time taken to complete tasks
- Number of tasks completed within a deadline
- Error rates or accuracy of work
Example of KPIs for Customer Support Team:
| Agent | Tickets Handled | Response Time (mins) | Resolution Rate (%) |
| Mark | 100 | 10 | 95% |
| Clara | 85 | 15 | 98% |
| Tony | 90 | 12 | 93% |
2. Qualitative Measures of Productivity
Quantitative measures alone may not give a complete picture of employee productivity, especially in jobs requiring critical thinking, creativity, or collaboration. Qualitative measures help assess these aspects:
2.1. 360-Degree Feedback
360-degree feedback gathers performance feedback from supervisors, peers, subordinates, and sometimes customers. This method provides a holistic view of an employee’s productivity, including soft skills such as communication, teamwork, and leadership.
360-Degree Feedback Survey Example:
| Employee | Peer Rating | Manager Rating | Self Rating | Average Rating |
| Sarah | 4.5 | 4.7 | 4.2 | 4.47 |
| John | 4.0 | 4.2 | 3.9 | 4.03 |
| Michael | 3.8 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 3.83 |
2.2. Self-Evaluations
Self-evaluations allow employees to reflect on their work, set personal goals, and identify areas for improvement. When combined with manager evaluations, self-assessments help ensure that both parties are aligned on productivity expectations.
Sample Self-Evaluation Questions:
- What were your key achievements this quarter?
- How did you overcome obstacles in your work?
- What skills would you like to develop further?
2.3. Customer Satisfaction Scores (CSAT)
For employees in customer-facing roles, customer satisfaction can provide valuable insights into their productivity. High CSAT scores often indicate effective employee performance.
CSAT Example (scale 1-5):
| Customer Support Agent | Average CSAT Score |
| Emily | 4.8 |
| Robert | 4.5 |
| Lily | 4.9 |
3. Time Management and Task Tracking
Another way to measure productivity is through time management tools and task tracking. These methods ensure that employees are using their time effectively and completing tasks on schedule.
3.1. Time Tracking Software
Tools like Trello, Asana, or Monday.com allow managers to monitor how much time employees spend on various tasks and projects.
Example Task Completion Analysis:
| Employee | Task | Estimated Time | Actual Time | Completion (%) |
| Emma | Project Research | 5 hours | 4.5 hours | 90% |
| Jake | Report Writing | 3 hours | 3.5 hours | 100% |
| Amanda | Data Analysis | 6 hours | 7 hours | 85% |
3.2. Task Completion Rates
Measuring task completion rates, especially in project-based roles, offers insight into how efficiently employees work.
Example:
| Employee | Tasks Assigned | Tasks Completed | Completion Rate (%) |
| James | 15 | 14 | 93.33% |
| Alex | 20 | 19 | 95% |
| Olivia | 12 | 12 | 100% |
4. Productivity Metrics for Remote Work
With the rise of remote work, measuring productivity in non-office settings has become a challenge. However, several methods have been effective for tracking productivity in remote environments.
4.1. Goal Setting and OKRs (Objectives and Key Results)
For remote teams, setting clear goals and key results (OKRs) can be a strong measure of productivity.
Sample OKR Framework:
| Objective | Key Result | Progress (%) |
| Increase Product Knowledge | Complete 3 training sessions | 75% |
| Improve Client Retention | Achieve 85% customer satisfaction rate | 90% |
| Boost Team Collaboration | Conduct weekly team huddles | 100% |
4.2. Communication Tracking
In remote work, collaboration tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams provide insights into how effectively employees communicate, resolve issues, and complete tasks together.
Example Communication Analysis:
| Employee | Messages Sent | Meetings Attended | Tasks Completed |
| Jessica | 120 | 5 | 10 |
| Ryan | 85 | 3 | 8 |
5. Employee Engagement and Well-being as Productivity Indicators
Research suggests that employee engagement and well-being are closely tied to productivity. Engaged employees are more likely to be productive, while burnout or dissatisfaction can lead to drops in performance.
5.1. Employee Engagement Surveys
Regular engagement surveys help assess how connected employees feel to their work and the organization.
Engagement Survey Example:
| Question | Average Score (1-5) |
| Do you feel motivated to perform your best at work? | 4.2 |
| Do you have the resources to do your job effectively? | 4.5 |
| Are you satisfied with your work-life balance? | 3.9 |
5.2. Absenteeism and Turnover Rates
High levels of absenteeism and employee turnover often signal low engagement, which can harm productivity.
Absenteeism and Turnover Example:
| Department | Absenteeism Rate (%) | Turnover Rate (%) |
| Sales | 2.5 | 5.3 |
| Marketing | 1.2 | 3.0 |
| IT | 0.9 | 2.0 |
Conclusion
Measuring employee productivity involves a blend of quantitative and qualitative approaches, tailored to the specific job roles and organizational context. Using a combination of output-based metrics, time management tools, and employee engagement assessments provides a well-rounded view of productivity. The right balance of these metrics helps managers identify areas for improvement, optimize workflows, and drive employee performance. By consistently monitoring and analyzing productivity data, organizations can foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Table: Summary of Productivity Measurement Methods
| Method | Type | Use Case |
| Output Per Hour (OPH) | Quantitative | Manufacturing, repetitive tasks |
| Sales Metrics | Quantitative | Sales, business development |
| KPIs | Quantitative | All departments |
| 360-Degree Feedback | Qualitative | Leadership, managerial roles |
| Time Tracking Software | Quantitative | Remote work, project-based roles |
| Employee Engagement Surveys | Qualitative | Organizational engagement, human resources |
By adopting a multifaceted approach, businesses can improve not only the accuracy of productivity measurement but also employee satisfaction and long-term success.
